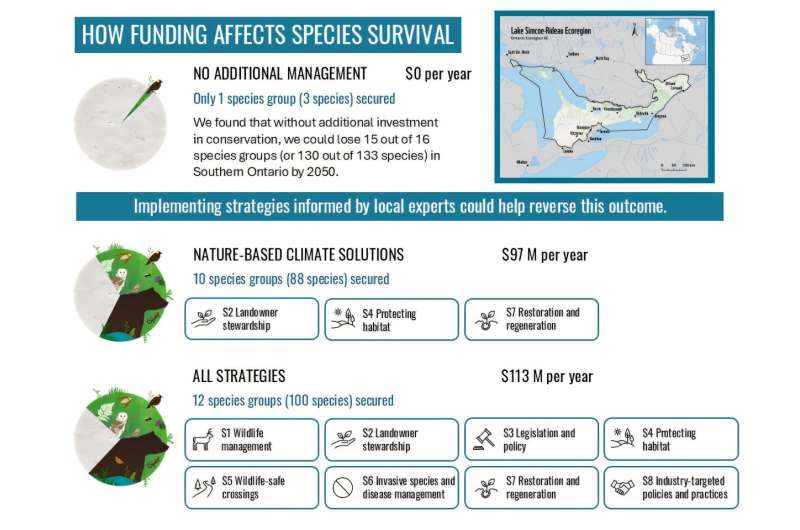
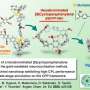
The intersection of non-Hermitian physics and topological photonics has led to groundbreaking research in the field of laser technologies. Recent studies indicate that zero lasing modes do not always exhibit topological characteristics, a finding that could significantly influence the design of more robust laser systems.
This research has emerged from a collaboration among various academic institutions and research groups. By investigating the properties of lasers in non-Hermitian environments, scientists are re-evaluating assumptions about the relationship between lasing modes and topological properties. The implications of these findings may extend beyond theoretical physics and could pave the way for practical applications in optical technologies.
Understanding Non-Hermitian Physics
Non-Hermitian physics, which deals with systems that do not conserve energy, has become a focal point for researchers exploring new phenomena in laser technology. Unlike traditional systems, non-Hermitian systems can exhibit unique behaviors such as exceptional points and non-reciprocal light propagation. These properties can enhance the stability and performance of laser systems, making them more efficient and versatile.
The ongoing research aims to clarify the conditions under which zero lasing modes can be classified as topological. Traditionally, it was thought that these modes must exhibit certain protective features to qualify as topological. However, recent experimental evidence suggests that this classification may not hold true in all cases, challenging existing theories.
Implications for Future Laser Technologies
The potential applications of these findings are broad. By understanding how zero lasing modes can operate outside the traditional topological framework, researchers could develop new types of lasers that are more resilient to external perturbations. This advancement could have significant implications in fields such as telecommunications, medical imaging, and quantum computing.
As researchers continue to explore the convergence of non-Hermitian physics and topological photonics, the possibilities for innovation appear promising. The research community is keenly watching how these findings will influence the next generation of laser technologies, as the quest for more robust and efficient systems progresses.
In summary, the investigation into the relationship between zero lasing modes and topological properties is revealing new dimensions in laser physics. As scientists delve deeper into this complex interplay, the potential for transformative advancements in optical technologies becomes increasingly apparent.