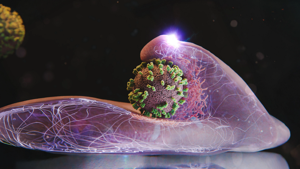
In a groundbreaking study, researchers from Switzerland and Japan have successfully captured the precise moment a person catches the flu. This significant advancement, published in October 2023, utilizes high-resolution imaging techniques to observe the infection process in real-time. The findings may lead to the development of antiviral therapies that are more targeted and effective.
The research team, based at renowned institutions in both countries, focused on the mechanisms through which the flu virus infects human cells. By employing advanced imaging technology, they were able to visualize interactions between the virus and host cells at an unprecedented level of detail. This clarity allows scientists to identify critical steps in the infection process, which can inform the design of future antiviral treatments.
Understanding how the flu virus operates is crucial, especially given its capacity to mutate rapidly and evade existing vaccines. The researchers’ observations revealed specific moments when viral particles successfully enter human cells, a process that occurs in a matter of seconds. Such insights can significantly enhance the development of therapies that target these critical stages of infection.
Additionally, the study highlights the potential for high-resolution imaging technology to revolutionize the field of virology. By capturing real-time interactions, scientists can gain a clearer understanding of viral behavior, paving the way for innovative treatment strategies. The research underscores the importance of international collaboration, with the combined expertise of Swiss and Japanese scientists proving instrumental in achieving these results.
As the flu remains a significant public health concern worldwide, this research offers hope for more effective responses to viral infections. The findings may also extend beyond the flu, potentially influencing how other viral diseases are treated in the future.
With flu season approaching, the implications of this study are particularly timely. Healthcare professionals and researchers alike are eager for advancements that could lead to improved prevention and treatment options. The ability to observe viral infections at such a granular level marks a significant leap forward in medical science.
In conclusion, the work conducted by these researchers not only sheds light on the flu virus but also sets the stage for future innovations in antiviral therapies. By understanding the infection process in high resolution, scientists are better equipped to combat the flu and other viral threats, ultimately benefiting public health on a global scale.