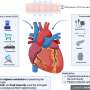
A recent analysis published in the Mayo Clinic Proceedings reveals that financial strain and food insecurity significantly contribute to accelerated biological aging of the heart. This study highlights the growing impact of social determinants of health (SDoH) on cardiovascular health, suggesting that these factors may pose a greater risk than traditional health indicators.
The research identifies financial hardship and lack of access to sufficient, nutritious food as the strongest drivers of increased mortality risk and cardiac aging. These findings underscore the complexity of health risks associated with social conditions, emphasizing the need for a holistic approach to patient care.
Understanding the Impact of Social Determinants
The study indicates that individuals facing financial difficulties and food insecurity are at a heightened risk for cardiovascular issues. Researchers analyzed various social risk factors and their relationship with biological aging, revealing that these elements often intertwine with traditional risk factors such as high blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
According to the study, the effects of financial strain on health can manifest in various ways, including increased stress levels and reduced access to healthcare services. Similarly, food insecurity can lead to poor dietary choices, further compounding the risk for heart-related illnesses.
The implications of these findings are profound, highlighting the necessity for targeted preventive interventions. Healthcare professionals are urged to integrate assessments of social determinants into routine patient evaluations. By recognizing how economic and social factors influence health, clinicians can develop more effective, patient-centered care strategies.
Call for Action and Future Directions
The researchers advocate for a multi-faceted approach to tackle these pressing issues. Addressing financial burden and food insecurity could lead to significant improvements in cardiovascular health outcomes. Public health policies should prioritize initiatives that alleviate these social determinants, potentially reducing the incidence of cardiac events and related mortality.
This study serves as a critical reminder of the importance of considering broader social factors in health assessments. As healthcare systems evolve, integrating these findings into practice will be essential for improving overall patient well-being and reducing health disparities.
The findings from the Mayo Clinic Proceedings call for urgent action from policymakers, healthcare providers, and community leaders alike. By working collaboratively to address the root causes of financial strain and food insecurity, the healthcare community can help foster a healthier population and ultimately save lives.