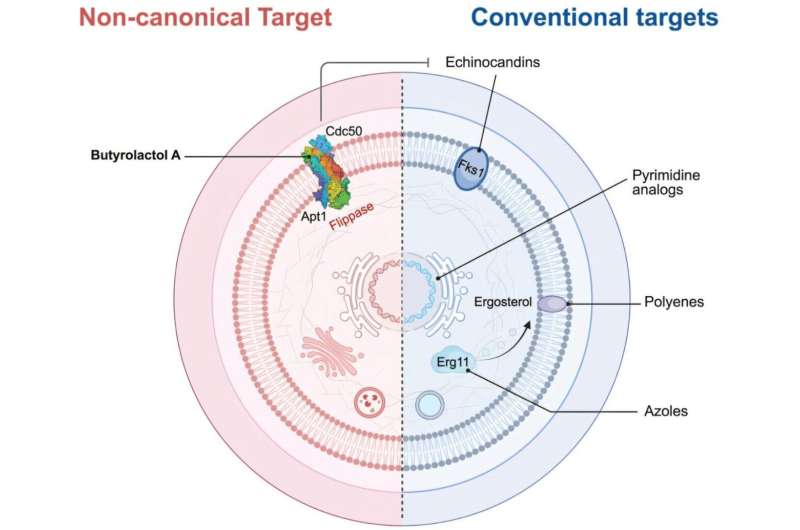
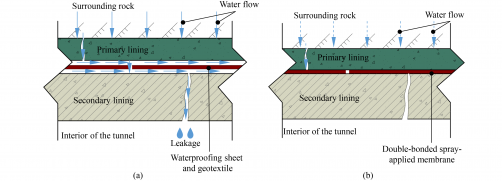
Enzymes serve as essential catalysts in biological processes, enabling the construction and breakdown of molecules, the replication of DNA, and the digestion of food. Traditionally, scientists have focused on creating drugs that inhibit or block these molecular machines to combat diseases such as infections and cancer. Recent discussions among researchers suggest that, for certain conditions, a different approach may be necessary—one that looks to enhance rather than inhibit enzyme activity.
Reevaluating the Role of Enzymes in Disease Treatment
The prevailing strategy in drug development has been to slow down or prevent enzymes from functioning. This tactic has proven effective for various diseases, particularly in stopping the spread of cancer cells or halting the progression of infections. However, emerging research indicates that enhancing the activity of specific enzymes could also play a crucial role in treatment strategies.
For instance, certain metabolic disorders might benefit from increased enzyme activity that promotes the breakdown of toxic substances in the body. This shift in focus aims to explore how modifying enzyme function can lead to improved therapeutic outcomes. Researchers are investigating how this approach can be applied to a range of diseases, from genetic disorders to chronic illnesses.
New Frontiers in Enzyme Research
The field of enzyme research is rapidly evolving, with scientists at various institutions conducting studies to better understand these complex molecules. For example, advancements in molecular biology techniques are allowing researchers to visualize enzyme interactions in real time. This capability could lead to breakthroughs in how drugs are designed and how they function within the body.
In addition to studying enzymes, researchers are also examining the impact of environmental factors and genetic variations on enzyme activity. This comprehensive approach could provide insights into personalized medicine, offering tailored treatments that consider individual patient profiles.
As scientists continue to push the boundaries of enzyme research, they are laying the groundwork for innovative therapies that could redefine how diseases are treated. The potential to shift from inhibition to enhancement represents a significant paradigm change, one that could lead to more effective and targeted treatments.
The next steps in this research will involve collaborative efforts among scientists, clinicians, and pharmaceutical companies to translate these findings into practical applications. The objective is clear: to develop new drugs that not only block harmful enzymes but also harness their power to combat disease effectively.