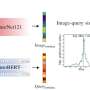
For over 25 years, the International Space Station (ISS) has been a hub of scientific innovation and research, enabling humans to live and work continuously in orbit. Since its first module was launched in 1998, the ISS has served as a unique laboratory for conducting a wide range of experiments, fundamentally advancing our understanding of life both on Earth and in space.
The research conducted aboard the ISS has far-reaching implications. Scientists from various disciplines have studied how to grow food in microgravity, sequenced DNA, and researched diseases that affect the human body. These studies not only enhance our knowledge but also pave the way for future space exploration, especially in preparation for potential missions to Mars and beyond.
Transforming Life on Earth Through Space Research
Experiments aboard the ISS have led to significant developments in agriculture, biotechnology, and medicine. For instance, researchers have successfully grown various crops, which could be crucial for sustaining long-duration missions. The ability to cultivate food in space is instrumental for future interplanetary travel, ensuring astronauts have access to fresh produce.
Additionally, the ISS has been vital in understanding diseases. By studying pathogens in microgravity, scientists can gain insights into how they behave differently than they do on Earth. This research can lead to improved treatments and preventive measures for health issues that affect people globally.
The international cooperation on the ISS stands as a testament to what can be achieved when nations work together. Agencies such as NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), and the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) have collaborated to enhance scientific knowledge. This partnership has not only advanced space exploration but has also fostered goodwill among nations.
The Future of Exploration and Technology
Looking ahead, the ISS will continue to play a pivotal role in preparing humanity for its next frontier. Upcoming experiments are set to focus on advanced technologies, including new life support systems and sustainable energy sources, which are essential for long-term missions in space.
The ISS has also served as a testing ground for new technologies that can be used on Earth. Innovations developed for space applications often find their way into everyday life, improving technology in sectors such as healthcare, environmental monitoring, and materials science.
As we celebrate this remarkable milestone, the ISS reminds us of the potential for human ingenuity and collaboration. The knowledge gained over the past quarter-century will have lasting impacts, guiding future generations in their quest for exploration, discovery, and understanding of our universe.