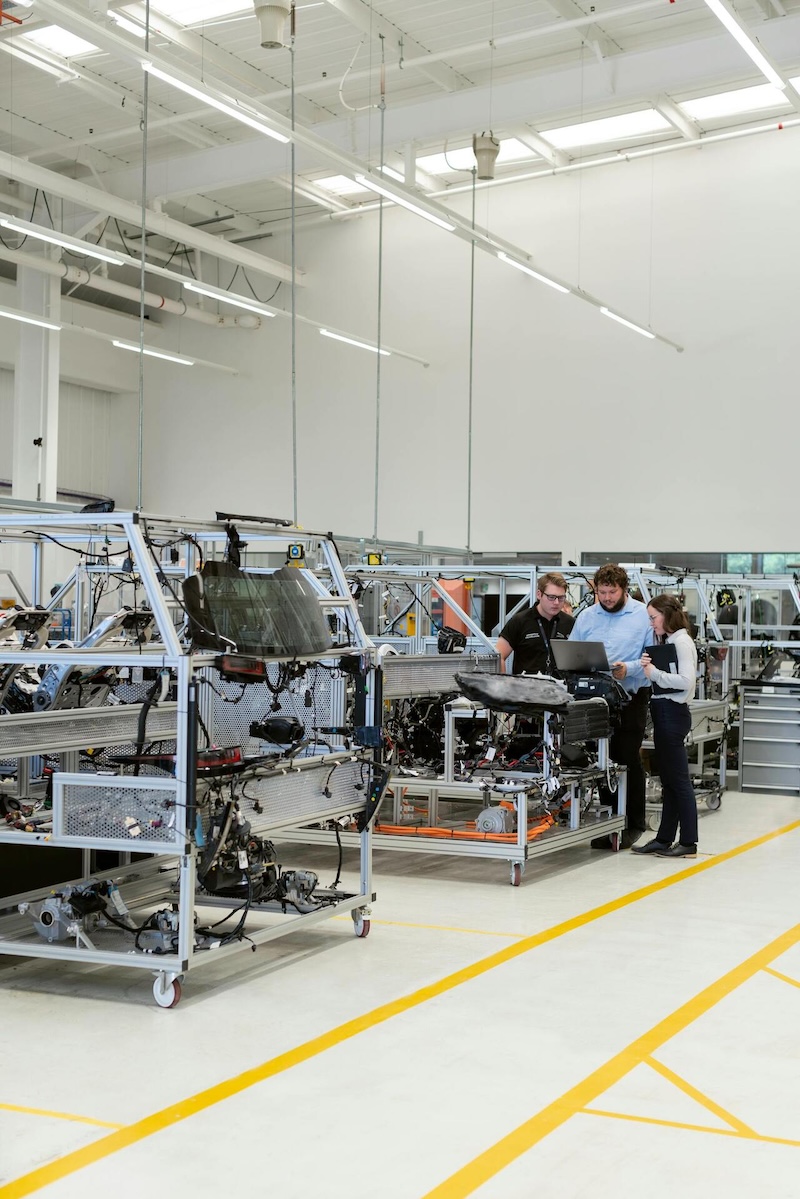
Industrial automation has undergone a significant transformation over the past decade, shifting from pre-programmed movements to more dynamic and intelligent processes. The integration of 3D guidance systems has been a pivotal development in enhancing the capabilities of industrial robots, allowing for greater flexibility and precision in manufacturing environments.
Transition from 2D to 3D Guidance
Historically, the manufacturing sector relied heavily on 2D vision systems for robotic guidance. This approach, while functional, posed limitations in adaptability and accuracy. As technology advanced, the shift towards 3D guidance gained momentum, enabling robots to interpret their surroundings with a depth of perception previously unattainable. This evolution has allowed robots to navigate complex environments and perform intricate tasks with improved efficiency.
The transition to 3D guidance systems began gaining traction while 2D was still prevalent. By incorporating advanced vision systems, robots can now assess spatial relationships and adjust their movements in real-time. This capability is particularly beneficial in industries requiring high precision, such as electronics and automotive manufacturing.
Impact on the Manufacturing Industry
The implementation of 3D guidance technology is reshaping the manufacturing landscape. Robotic systems equipped with these capabilities are not only enhancing productivity but also improving safety in workplace environments. For example, robots can now work alongside human operators without the need for protective barriers, reducing the risk of accidents and injuries.
According to a report by Markets and Markets, the global industrial robotics market is expected to reach $63.3 billion by 2023, driven in part by advancements in 3D guidance technology. This growth reflects a broader trend toward automation and intelligent manufacturing, where robots are increasingly seen as essential partners rather than mere tools.
Furthermore, the flexibility afforded by 3D guidance allows manufacturers to adapt quickly to changing demands. As production processes become more complex and customized, the ability of robots to easily reconfigure their operations will be crucial for maintaining competitiveness in the global market.
In conclusion, the shift from 2D to 3D guidance systems marks a significant milestone in the evolution of industrial robotics. By enhancing accuracy, safety, and flexibility, this technology is not only transforming manufacturing processes but also redefining the role of robots in the workplace. As industries continue to embrace these advancements, the future of automation looks increasingly promising.