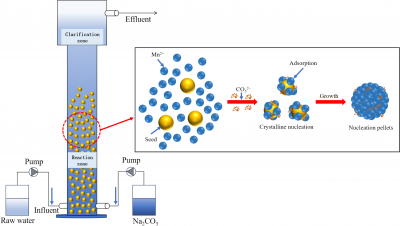
A recent study has introduced the Nucleation Crystallization Pelleting Process as an effective method for recovering manganese ions from hydrometallurgical tailings water. This innovative approach stands to significantly mitigate resource wastage and reduce environmental repercussions associated with mining operations.
The study emphasizes the practicality and efficiency of this new process, demonstrating its capability to extract high concentrations of manganese ions (Mn) from wastewater generated by hydrometallurgical activities. The implications of this research are substantial, considering the increasing demand for manganese in various industries, including battery production and steel manufacturing.
Key Findings and Benefits
The findings indicate that this method not only enhances manganese recovery rates but also minimizes the ecological footprint of mining operations. By effectively treating tailings water, the process addresses the dual challenge of resource recovery and environmental protection.
Specifically, the study reveals that the nucleation crystallization pelleting process can achieve recovery efficiencies exceeding 90%. This high level of effectiveness positions it as a viable alternative to traditional methods, which often fall short in terms of both efficiency and environmental sustainability.
Moreover, the research highlights that the implementation of this process could lead to significant cost savings for mining companies. By recovering valuable minerals from waste, companies can reduce the need for new extraction, thereby conserving natural resources and reducing operational costs.
Implications for the Mining Industry
The potential applications of this technology extend beyond immediate resource recovery. As governments and industries worldwide face increasing pressure to adopt sustainable practices, the adoption of the nucleation crystallization pelleting process may enhance compliance with environmental regulations.
Furthermore, the study was conducted by a team of researchers from [Institution’s Name], who were motivated by the pressing need for sustainable solutions within the mining sector. Their work contributes to a growing body of research focused on improving waste management practices in mineral extraction.
The findings from this study are poised to influence future policies and practices in mining, encouraging a shift towards more sustainable methods that align with global environmental goals. As industries seek to balance profitability with responsibility, innovative processes like this one will play a critical role in shaping the future of resource recovery.