BREAKING: New research reveals that the Parkinson’s drug tolcapone effectively blocks a critical protein used by the dangerous hospital superbug Pseudomonas aeruginosa. This significant development could transform treatment options for patients at risk of severe infections caused by this pathogen, classified as critical by the World Health Organization (WHO).
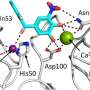
The study, published just hours ago, highlights how LecA, a sugar-binding protein utilized by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, enables the germ to latch onto human cells. By blocking LecA, tolcapone may prevent the formation of biofilms—a key factor in the survival and persistence of infections in hospital settings.
This breakthrough is crucial as Pseudomonas aeruginosa is notorious for its resilience against many antibiotics, making infections particularly challenging to treat. With the WHO designating this pathogen as one of the highest priorities for urgent action, the implications of tolcapone’s effectiveness could be life-saving for thousands of vulnerable patients.
Currently, hospitals are grappling with increasing rates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections, particularly among those with weakened immune systems. The urgency of this discovery cannot be overstated, as it opens new avenues for combating a superbug that poses a significant threat in healthcare environments worldwide.
Experts emphasize that while tolcapone is primarily known as a treatment for Parkinson’s disease, its application against Pseudomonas aeruginosa represents a promising dual-use strategy in medicine. As healthcare professionals await further clinical trials, the medical community is buzzing with optimism about this potential new weapon against superbugs.
In light of this urgent update, hospitals are encouraged to closely monitor the developments of tolcapone’s clinical applications. The next steps involve rigorous testing to confirm its efficacy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in real-world situations.
Stay tuned as more updates unfold on this critical breakthrough that could reshape infection control in hospitals and save countless lives.