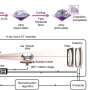
Scientists at the University of California, Berkeley, have unveiled an innovative imaging technique that allows for the observation of metal crystal growth within liquid metal. This development could significantly enhance hydrogen production methods, which are vital for advancing clean energy technologies. The research, conducted in collaboration with the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, offers a new perspective on the processes involved in metal crystallization.
The imaging technique enables researchers to visualize the formation of metal crystals in real-time. By applying this method, scientists can better understand how the crystals grow and how impurities are expelled during the process. This is akin to dissolving sugar in hot water, where cooling the solution leads to the formation of pure sugar crystals while impurities remain dissolved. In this context, the new method may lead to more efficient hydrogen production by optimizing the conditions under which metal crystals form.
Understanding the dynamics of crystal growth is crucial for the hydrogen production industry. According to a report published in 2023, improved hydrogen generation techniques could lead to a reduction in costs associated with this clean energy source. Hydrogen is considered a key player in achieving global climate goals, and advancements in its production methods are essential for a sustainable future.
The research team utilized advanced imaging technologies to track the growth of metal crystals within a liquid metal environment. This breakthrough allows for the observation of crystal dynamics at unprecedented resolution, opening new avenues for research in materials science and energy production. The implications of this work extend beyond hydrogen production; the insights gained may also benefit other fields, including electronics and catalysis.
As the world increasingly turns to cleaner energy alternatives, the importance of efficient hydrogen production cannot be overstated. Hydrogen fuel cells have the potential to revolutionize transportation and power generation, but current production methods face challenges related to cost and efficiency. The findings from the University of California, Berkeley, could play a pivotal role in overcoming these hurdles.
In conclusion, the development of this imaging technique represents a significant advancement in the understanding of metal crystal growth and its applications in hydrogen production. With further research and development, this innovative approach may contribute to the broader goal of achieving sustainable energy solutions.