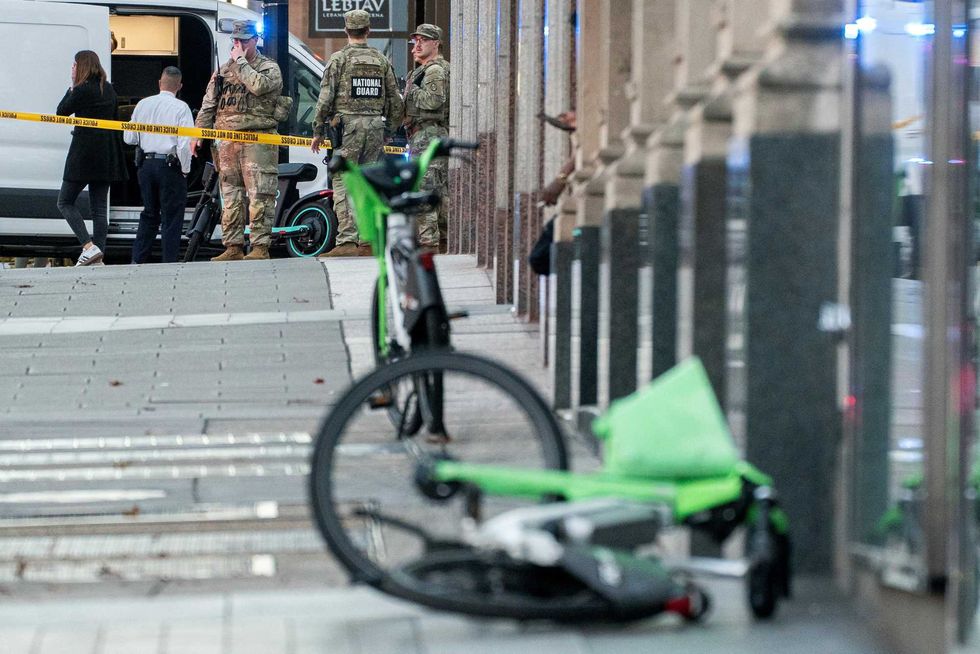
The deployment of National Guard troops in Washington, D.C., has raised significant safety and legal concerns following a federal judge’s ruling on the matter. On November 20, 2025, a judge deemed the deployment illegal, yet the troops remained in the capital, where they faced serious threats while on duty. This situation highlights the complex intersection of military operations and domestic law enforcement, a subject of ongoing debate.
In August, The Military Times, a publication recognized for its neutrality, criticized the decision to assign approximately 2,300 National Guard members to perform non-combat tasks such as lawn care. Analysts pointed out that these assignments placed the troops in a “heightened threat environment,” compromising their safety and impacting morale. Critics noted that such deployments contradicted the objectives set by Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth, who emphasized a focus on “lethality” and military readiness.
The deployment drew ire from various quarters, with foreign media outlets mockingly dubbing the troops “Trump’s lethal landscapers.” Critics, including former Defense Secretaries Lloyd Austin and Jim Mattis, expressed alarm over the politicization of the military under President Donald Trump. They issued a joint letter to Congress, warning against the implications of using troops for domestic law enforcement, which is prohibited under the Posse Comitatus Act unless specific conditions of insurrection are met.
The legal framework surrounding military involvement in domestic affairs is clear. The Posse Comitatus Act has disallowed military troops from engaging in law enforcement for over 150 years, except under certain circumstances, such as rebellion or extreme violence, which require activation of the Insurrection Act. Critics assert that Trump’s rationale for deploying troops—citing crime in Democratic-led cities and immigration initiatives—does not meet the legal threshold established by federal law.
The ramifications of this deployment were tragically illustrated when two National Guard members were shot outside a Washington, D.C., Metro station shortly after the judge’s ruling. The incident occurred on November 26, 2025, leading to one soldier’s death. Instead of addressing the situation with sensitivity, Trump shifted blame to President Joe Biden, alleging that the shooter was unvetted. This claim was quickly challenged by reports confirming that the suspect, Rahmanullah Lakanwal, had been thoroughly vetted by U.S. intelligence agencies.
Military advisers have consistently warned that placing American troops on domestic streets heightens their risk. A member of the California National Guard expressed concern via text message to the New York Times, stating that the assignment could lead to civilian casualties or potential threats to the troops themselves. Despite these warnings, Trump announced plans to send an additional 500 troops to D.C. and halt immigration from certain countries, further escalating tensions.
The ongoing situation underscores the critical distinction between military and law enforcement roles. The military’s primary mission is to defend against foreign threats, focusing on combat readiness and lethal capabilities, while law enforcement prioritizes civilian safety and de-escalation. Confusing these roles can lead to dangerous outcomes, both for service members and the civilian population.
As the debate continues over the appropriateness of military deployments in domestic settings, the implications for both the safety of troops and the legal framework governing such actions remain at the forefront of ongoing discussions.