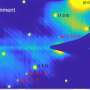
Astronomers have unveiled a remarkable shock wave surrounding a dead star known as RXJ0528+2838, a discovery made possible through the advanced imaging capabilities of the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope (VLT). This unexpected finding has left scientists puzzled, as current astrophysical models do not predict such structures around stars in the later stages of their life cycle.
The shock wave was formed when gas and dust ejected from the star collided with its surrounding environment. Such interactions are not uncommon, but the presence of this specific shock wave challenges existing theories regarding the behavior of dead stars. The discovery raises important questions about our understanding of stellar evolution and the complex dynamics that occur post-main sequence.
Unexpected Findings Challenge Stellar Evolution Models
Astrophysicists have long studied the processes surrounding dying stars, but the characteristics of the shock wave around RXJ0528+2838 defy the known mechanisms. According to research conducted using the VLT, the shock wave exhibits features that are not typically associated with a star in its current state. This anomaly suggests that there may be unrecognized interactions occurring in the surrounding medium that require further investigation.
The imaging of the shock wave not only showcases the capabilities of contemporary astronomical tools but also highlights the need for a reevaluation of theories concerning the interactions of stellar remnants with their environments. The observations were made in late 2023, marking a significant advancement in the field of astrophysics.
Astronomers involved in the study are now analyzing data and exploring potential explanations for this phenomenon. Possible factors include variations in the ejected material’s composition or the influence of external forces that could alter the expected behavior of the stellar remnants.
A Path Forward for Research and Understanding
As the scientific community grapples with these findings, the implications extend beyond the specific case of RXJ0528+2838. Understanding the dynamics of shock waves and their formation mechanisms can provide deeper insights into the life cycles of stars and the evolution of galaxies.
Further observational studies are planned, aiming to gather additional data on this unique shock wave and similar phenomena. By employing advanced techniques and instruments, astronomers hope to unlock the mysteries surrounding the interactions of dead stars and their environments.
The discovery serves as a reminder of the complexities of the universe and the continuous need for exploration and inquiry. As researchers delve into the enigma presented by RXJ0528+2838, the pursuit of knowledge about our cosmos remains both challenging and exhilarating.