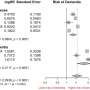
BREAKING: A new meta-analysis reveals alarming news for hospitalized patients. Research led by Wei Yu Chua from the National University of Singapore confirms that adults admitted to hospitals with infections have a staggering 50% higher risk of developing dementia.
The study, involving thousands of cases, underscores a critical health concern that affects millions globally. The findings were shared earlier today by Eng-King Tan, corresponding author and a prominent figure at both the National Neuroscience Institute and Duke-NUS Medical School in Singapore.
This urgent report sheds light on the intersection of acute medical conditions and long-term neurological health. With hospitalizations rising due to various infections, the implications of this research cannot be overstated. Patients and families must be aware of the potential long-term cognitive effects associated with infections that lead to hospitalization.
The analysis compiled data from multiple studies, focusing on the correlation between infection-related hospital stays and subsequent dementia diagnoses. This large-scale examination reveals that not only does infection pose an immediate threat, but it may also lead to serious cognitive decline later in life.
Healthcare professionals are now urged to consider these findings in their treatment protocols. The study calls for increased vigilance and monitoring of cognitive health in patients recovering from infections, especially in older adults who are already at risk for dementia.
As hospitals continue to manage rising infection rates, the urgency of this research is clear. It provides essential insights that could reshape how healthcare providers approach patient care both during and after hospitalization.
Looking ahead, public health authorities and medical institutions will need to address this concerning trend by enhancing preventive measures and monitoring cognitive outcomes in patients recovering from infections. The study serves as a wake-up call to prioritize not just immediate health but long-term cognitive well-being.
Stay tuned for more updates as experts continue to analyze and respond to these significant findings. The health community must act swiftly to integrate this crucial information into patient care strategies, ensuring that hospital stays do not lead to a higher risk of dementia for vulnerable populations.