BREAKING: A vital new study from the Çanakkale Onsekiz Mart University in Türkiye has just been released, shedding light on critical methods for preserving historical structures. This research, titled “Materials Characterization of Historical Structures: A Review,” addresses significant gaps in the understanding of building materials essential for cultural heritage conservation.
The survival of our historical buildings—key links to our art, architecture, and history—depends on effective preservation techniques. The study reveals that a comprehensive understanding of materials like natural stones and mortars is crucial for future generations. However, challenges persist, including inconsistent analysis methods and unclear guidelines for selecting appropriate characterization techniques.
In response to these challenges, the research team, led by Mertcan Demirel, Alican Topsakal, and Muhammet Gökhan Altun, systematically reviews the analytical methods employed in characterizing historical building materials. Their findings highlight four core categories of characterization techniques:
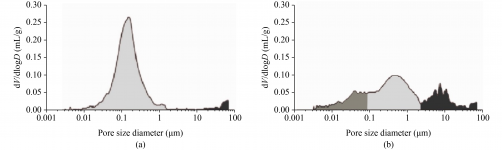
1. **Physical and Thermal Property Analysis:** Methods such as Mercury Intrusion Porosimetry (MIP) are utilized to assess porosity and water permeability. For example, mortars from Amaiur Castle exhibited two main pore size distributions ranging from 0.01–1 μm and 1–10 μm.
2. **Chemical Property Analysis:** Techniques like X-ray Diffraction (XRD) and X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) are pivotal in determining the mineral composition and elemental content of materials. Notably, high concentrations of lead and zinc have been detected in the black crusts of Seville Cathedral.
3. **Mechanical Property Analysis:** Non-destructive methods, including Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity (UPV) and Schmidt hammer tests, offer insights into the mechanical performance of structures without causing damage, ensuring the integrity of these historical landmarks remains intact.
4. **Visualization Techniques:** Advanced imaging methods, such as Scanning Electron Microscopy-Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (SEM-EDS), help uncover hidden defects and microstructural details, which are essential for effective restoration strategies.
The review also emphasizes the effectiveness of combining multiple methods to achieve reliable results, which can significantly lower costs in the engineering and architectural analysis of historical structures. This comprehensive approach is expected to provide a solid foundation for future scientific research and the development of restoration projects grounded in solid data.
The paper, authored by a dedicated team from the Department of Civil Engineering, focuses on historical benchmarks including structures from the Roman period in Portugal, 11th–14th century buildings in Spain, and Mamluk-period structures in Egypt.
FULL TEXT: The complete study is available at doi:10.1007/s11709-025-1222-3.
As the world grapples with the impacts of climate change and urban development on heritage sites, this urgent study offers a beacon of hope for preserving our cultural legacies. Researchers and conservationists are encouraged to explore these findings to enhance preservation efforts and ensure that future generations inherit these invaluable links to our past.